WHAT IS CLIMATE CHANGE AND HOW DOES IT AFFECT YOU?
Many people do not know what it really amounts to, either due to unreliable sources or deliberate misinformation, which has led to a series of myths about climate change. In these pages, we tackle the subject from an objective, scientific viewpoint, discussing the causes and consequences of climate change and how it should be tackled.
First, we need to clarify two concepts often mistaken for synonyms: climate change and global warming. There is an important difference between them, however, given that it is global warming that causes climate change. As the planet’s temperature rises more than it would naturally, the climate varies.
Although it is certain that Earth has naturally warmed up and got colder during other eras, such cycles have always been much slower, taking millions of years, whereas now, within a period of just 200 years, we are reaching levels that in the past brought about extinctions.
Before going over the causes and effects of climate change, let's explain why you don't care about climate change:
DISCOVER HOW TO AVOID CLIMATE CHANGE REALLY FAST
CAUSES AND CONSEQUENCES OF CLIMATE CHANGE
The main cause of climate change is global warming, which has many negative consequences on physical, biological and human systems, as well as other effects.
CAUSES OF CLIMATE CHANGE
Global warming is caused by the greenhouse effect, a natural process by which the atmosphere retains some of the Sun’s heat, allowing the Earth to maintain the necessary conditions to host life. Without the greenhouse effect, the average temperature of the planet would be -18ºC.
The problem is that daily human activities maximize the greenhouse effect, causing the planet’s temperature to increase even more.
CAUSES BEHIND GLOBAL WARMING
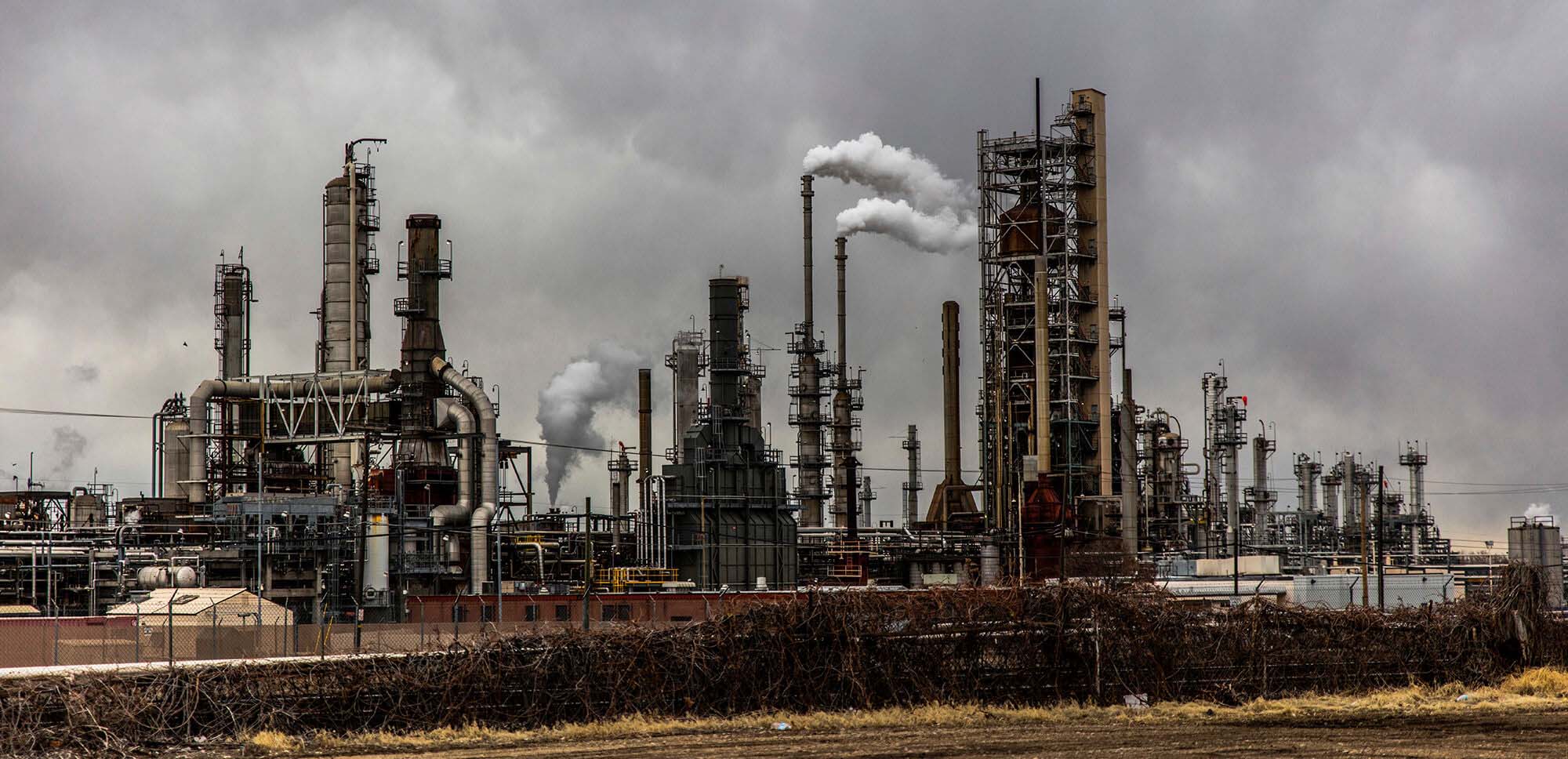

GREENHOUSE GASES
Carbon dioxide, Methane, Nitrogen oxide, HCFCs: caused mainly by the burning of fossil fuels in electricity generation, transport, heating, industry and construction. Also caused by livestock, agriculture (mainly rice farming), wastewater treatment and landfills among others.

DESTRUCTION OF LAND ECOSYSTEMS AND DEFORESTATION
Deforestation is one of the most important causes of climate change. The forests and rainforests are disappearing at breakneck speed. In the past 10 years, they have destroyed no less than 13 million hectares.

DESTRUCTION OF MARINE ECOSYSTEMS
The oceans are also carbon sinks, absorbing up to 50 % of CO2 The problem is that, when they reach their limit, the ocean acidifies and causes death and disease among marine flora and fauna.

POPULATION INCREASE
Human population is growing exponentially. Today, barely 250 years later, we are more than 7.7 billion and will continue growing until 2050 by at least another 2 billion. An increasingly numerous population needs more and more resources, which speeds up the increase in greenhouse gas emissions from all production processes.
WHEN DID HUMANS FIRST BEGIN TO CAUSE CLIMATE CHANGE?
Experts agree that the Industrial Revolution was the turning point when emissions of greenhouse effect gases entering the atmosphere began to soar. The Industrial Revolution was itself borne out of smaller revolutions: agricultural, technological, demographic, transport, finance… creating a new model of production and consumption.
From then onward, population growth (in 1750, there were fewer than 800 million people on Earth, whereas now we are over 7.5 billion), exploding resource use, increasing energy demand and production, mainly from fossil fuels, all saw the planet enter into what the scientific community have termed the Anthropocene period, a new geological era characterized by human impact on Earth.
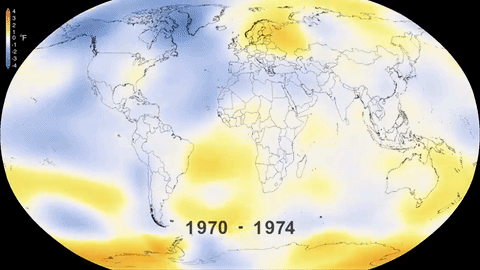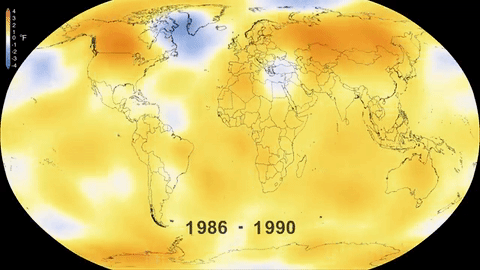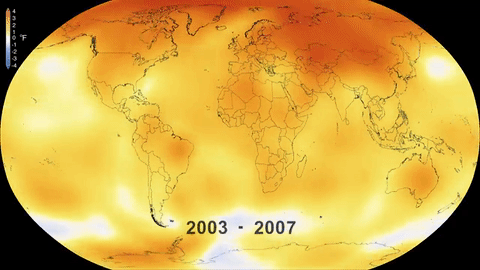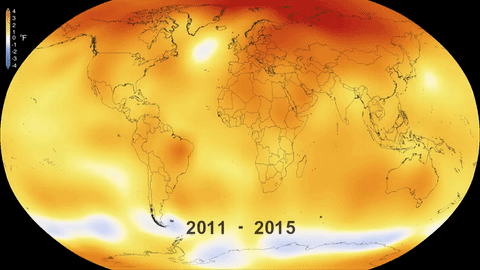
The main impact was the increase in the global temperature of the planet, which has risen 1.1°C since this period, although it is estimated that, by the end of the present Century, the thermometer could rise by 2.7 °C even if national commitments to reduce emissions are fulfilled.
GREENHOUSE EFFECT AND ANTHROPOCENE EXPLAINED IN 2 MINUTES
CONSEQUENCES OF CLIMATE CHANGE
The global temperature increase brings disastrous consequences, endangering the survival of the Earth’s flora and fauna, including human beings. The worst climate change impacts include the melting of the ice mass at the poles, which in turn causes rising sea level, producing flooding and threatening coastal environments through which small island states risk disappearing entirely.
Climate change also increases the appearance of more violent weather phenomena, drought, fires, the death of animal and plant species, flooding from rivers and lakes, the creation of climate refugees and destruction of the food chain and economic resources, especially in developing countries.
MAIN OBSERVED AND EXPECTED ENVIRONMENTAL EFFECTS

CHANGE IN ECOSYSTEMS AND DESERTIFICATION
Variations in life conditions in natural environments cause death, disease and massive migrations of species.
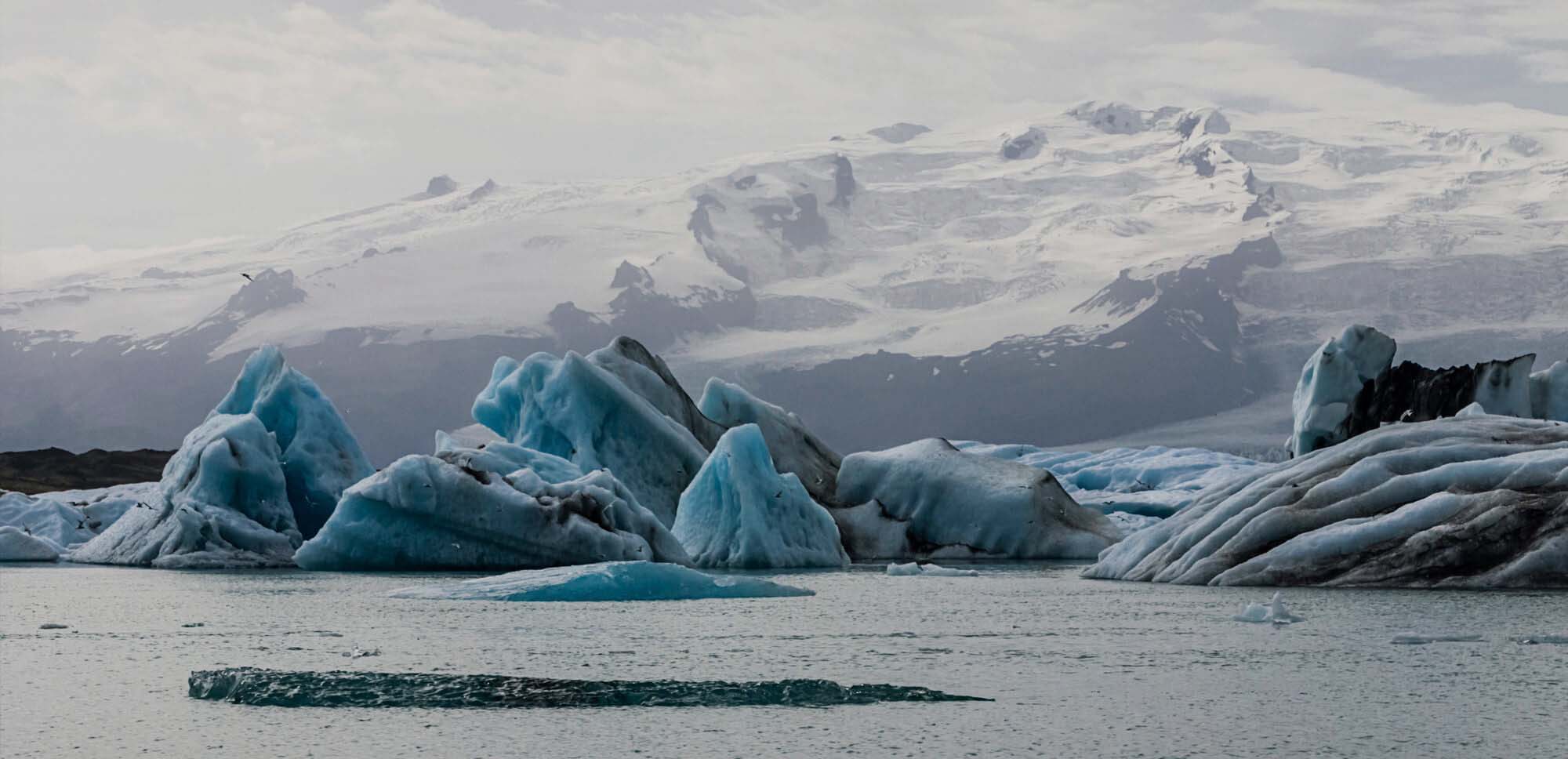

MELTING OF THE POLES AND RISING SEA LEVEL
Heat causes the melting of the ice at the poles, which increases the sea level and threatens to submerge coastal communities and small island states.
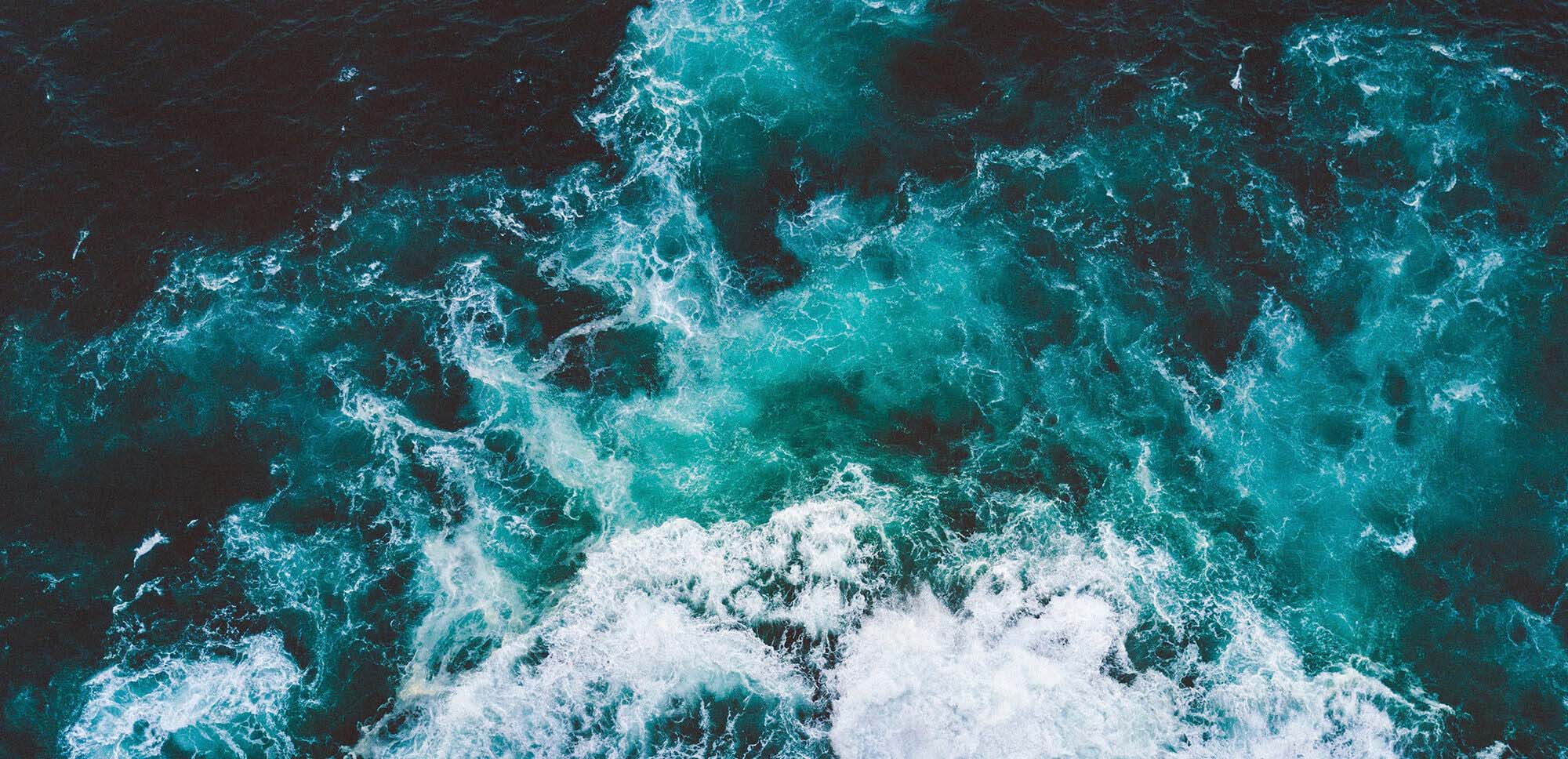

ACIDIFICATION OF THE OCEANS
The absorption of too much CO₂ causes death and disease among fish, algae, coral and other organisms in the sea.
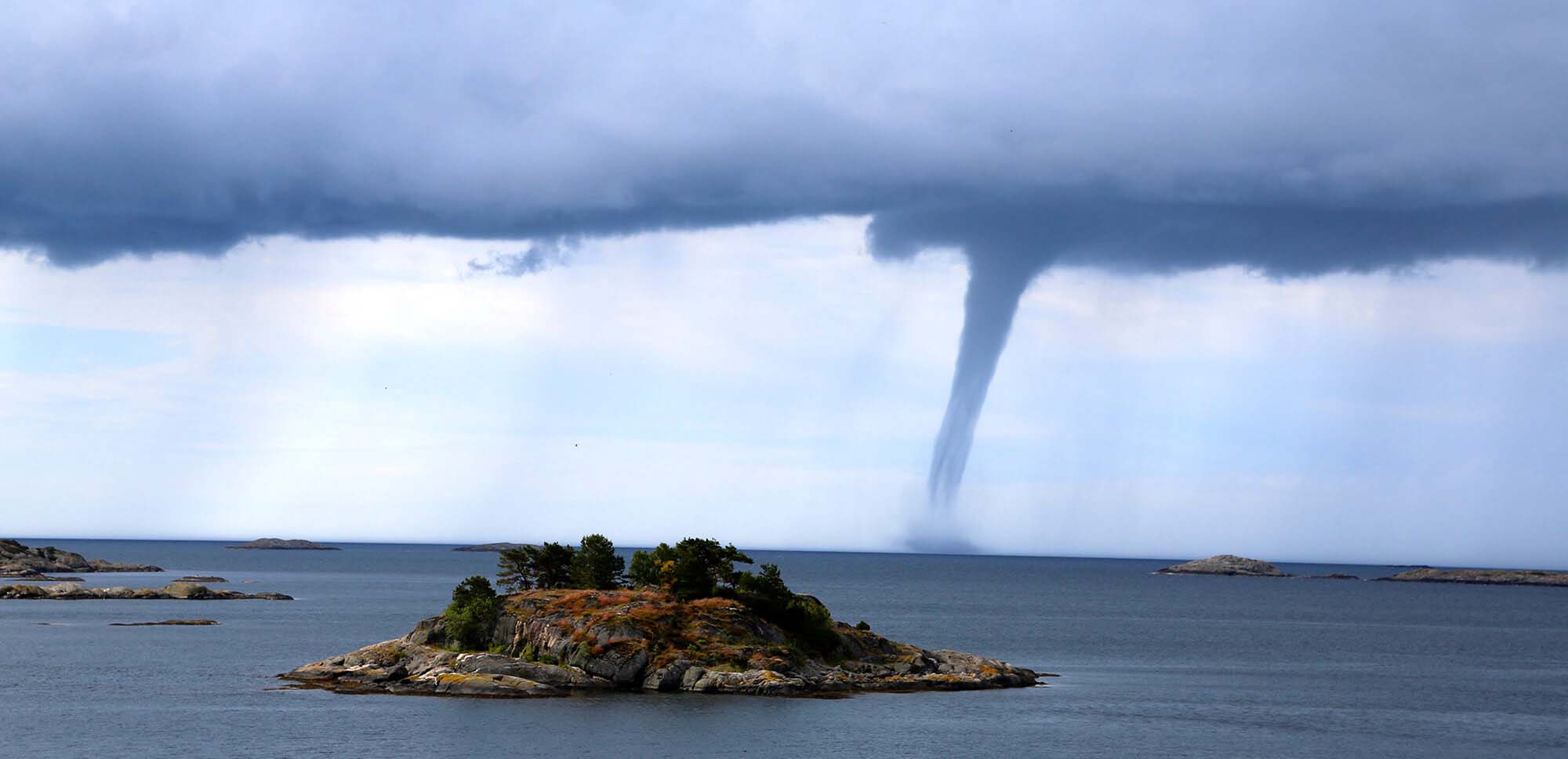

EXTREME WEATHER PHENOMENA
Hurricanes, cyclones, typhoons, drought, floods, rain and snow, all increase in their degree of violence due to global warming, causing more deaths, victims, refugees and material damage.

EXTINCTION OF SPECIES
Changes in ecosystems and desertification cause the death of between 10,000 and 50,000 species every year.

MASSIVE MIGRATIONS
The existence of climate refugees, still to be recognized by the United Nations, is a reality; it is estimated their number could reach one billion by 2050.
17 GOALS FOR A BETTER WORLD
These 17 objectives are interrelated and often the key to one's success will involve the issues most frequently linked to another.
They can be summarised as follows:
- Eradicate poverty and hunger, guaranteeing a healthy life
- Universalize access to basic services such as water, sanitation and sustainable energy
- Support the generation of development opportunities through inclusive education and decent work
- Foster innovation and resilient infrastructure, creating communities and cities able to produce and consume sustainably
- Reduce inequality in the world, especially that concerning gender
- Care for the environment combating climate change and protecting the oceans and land ecosystems
- Promote collaboration between different social agents to create an environment of peace and sustainable development.
ACCIONA'S COMMITMENT
THE FIGHT AGAINST CLIMATE CHANGE
ACCIONA considers the fight against climate change and its derivative effects a strategic priority. Aligned with the Sustainable Development Goals (SDG), especially with n. 13 - climate action- the company works to mitigate greenhouse gas emissions in order to contribute to the progress of society and respond to the main challenges of sustainable development in the field of infrastructure, water and energy, leading the transition to a low carbon economy.